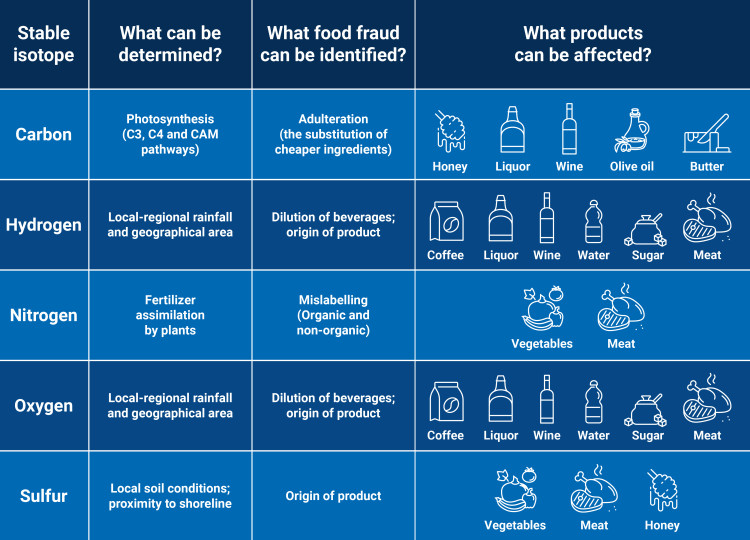
Food fraud can be defined as any intentional action, taken to deceive customers about the quality and content of the food products for financial gain. The selling of fake food around the world has become a highly lucrative illegal activity. While estimating the global impact is hard because it is designed to avoid detection, some experts are assessing that it could represent 40 billion dollars a year.
It is important for consumers to be sure that the quality and safety of food they buy is guaranteed. Many people prefer goods from certain brands due to their reputation for good quality. Some may even be ready to pay premium prices for their characteristics and ingredients. This attracts fraudsters, who try to turn a profit by replacing high quality ingredients with cheaper ones and pocketing the price difference.
Mitigating the risk of food fraud can be difficult. Fraud may happen at any stage of the supply chain, and in some cases, it cannot be detected without special equipment. In developing countries, the problem is aggravated by the lack of technical capacity to detect food fraud.