If you would like to learn more about the IAEA’s work, sign up for our weekly updates containing our most important news, multimedia and more.

Nuclear Explained - Environment
Nuclear Explained
What is Soil Erosion? How Can Nuclear Techniques Help to Identify and Mitigate it?
On World Soil Day, the IAEA highlights how nuclear and isotopic techniques help determine soil fertility and inform decisions about soil management and conservation. Read more →
What Are Particle Accelerators?
Particle accelerators produce and accelerate beams of charged particles, such as electrons, protons and ions, of atomic and sub-atomic size. Read more →
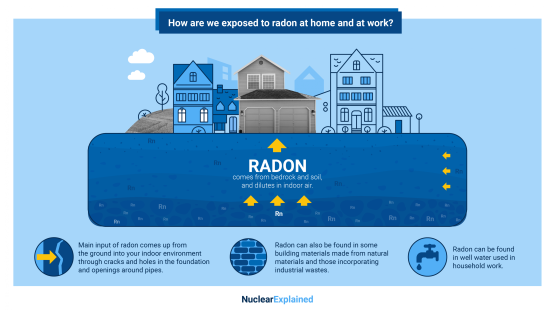
What is Radon and How are We Exposed to It?
One source of natural radiation that presents a danger is radon — a radioactive gas with no colour, smell or taste. It is released from bedrock material and passes through the soil. Read more →
Nuclear Explained – What is Ocean Acidification?
The ocean is both a source of oxygen and a sink for carbon dioxide (CO2). It absorbs about one fourth of all CO2 emissions. While this leaves less CO2 in the atmosphere and mitigates climate change, it makes the ocean more acidic. Read more →
What is Mutation Breeding?
Plant mutation breeding, also called variation breeding, is a method that uses physical radiation or chemical means to induce spontaneous genetic variation in plants to Read more →
- 1 of 3
- next ›