The IAEA has released its annual edition of the Country Nuclear Power Profiles (CNPP), documenting the status and development of nuclear power programmes worldwide as of the end of 2017.
The publication summarizes organizational and industrial aspects of nuclear power programmes, including information about relevant legislative, regulatory and international framework, in 50 countries, including 30 that are currently operating nuclear power plants, and 20 with past or planned nuclear power programmes.
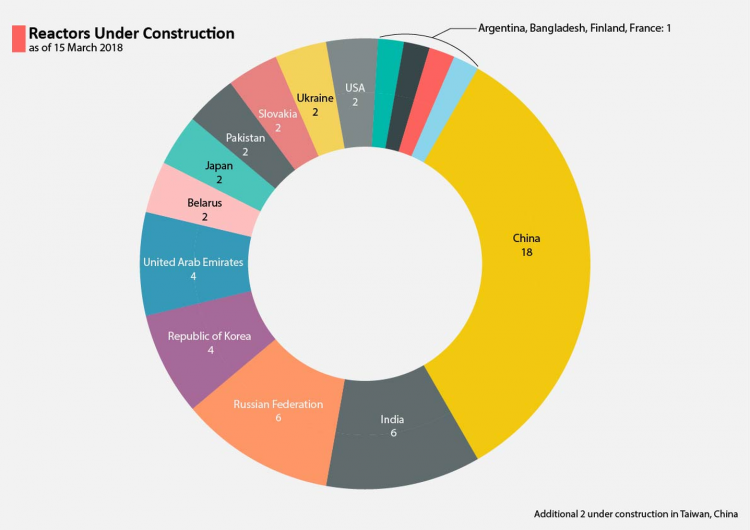
Nuclear power currently provides about 11% of the world’s electricity, with 12 countries using nuclear power for at least 30% of their national electricity generation. As of today, there are 449 operational nuclear power reactors in 30 countries, with 56 others under construction in 15 countries.
“The publication serves as an important resource not only for researchers, but also for decision makers and the wider public,” said Pal Vincze, Head of the IAEA’s Nuclear Power Engineering Section. “It is one of the few avenues through which Member States can provide information regarding their energy, economic and regulatory policies to promote transparency of their nuclear power programmes through a coordinated and vetted publication.”
The profiles provide a descriptive overview of the overall economic, energy and electricity situation in each country, with its nuclear power framework. Statistical data about nuclear plant operations, energy and electricity use are drawn from national contributions as well as IAEA data bases and World Development Indicators of the World Bank.
The 2017 edition outlines activities and summaries of 30 countries with nuclear power programmes, 14 of which are actively expanding their fleets and 6 others considering possible expansion. Two newcomers are planning to start operating their first nuclear power reactors in 2018: Belarus and the United Arab Emirates.
Member States can directly provide information regarding their respective energy, economic and regulatory policies to promote transparency of their nuclear power programme infrastructure, through a coordinated and vetted publication.