Nuclear medicine is a field of medicine that applies nuclear technology in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases. Today, nuclear medicine offers procedures that are essential for the evaluation of cancer, heart diseases and neurological diseases as well as illnesses involving thyroid, kidneys, bone, gastrointestinal systems and respiratory systems. Nuclear medicine health professionals include nuclear medicine physicians, nuclear medicine technologists, medical physicists and radiopharmacists, who work in a multidisciplinary team covering all facets of patient care and safety.
Although nuclear medicine is common in the developed world, a shortage of qualified staff hinders the advancement of this field of medicine in developing countries, depriving patients of appropriate diagnosis and treatment for many health problems. In addition, continuous development in nuclear medicine requires constant training to maintain and update knowledge and skills in any new procedures and technologies. To address this gap in human resources, and to enhance national capabilities in the diagnosis and treatment of disease using nuclear techniques, many of the IAEA's technical cooperation projects focus on the education and training of health professionals in nuclear medicine, building human resource capacities in all areas of nuclear medicine through fellowships, scientific visits and expert missions.
Four years ago, for example, a regional TC project (RAF/6/038, 'Promoting Regional and National Quality Assurance Programmes for Medical Physics in Nuclear Medicine') was initiated to promote human resource development and recognition of the medical physics profession in Africa. With the support of this and other national projects, medical physics is today recognized as a profession in Burkina Faso, Egypt, Ghana, Kenya, Madagascar, Mauritius, Nigeria, South Africa, Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda and Zimbabwe. In addition, academic training programmes are now in place in Algeria, Egypt, Ghana, Libya, Morocco, Nigeria, South Africa, Sudan and Tunisia. Work is ongoing to harmonize academic and clinical training programme in these countries.
Over the past ten years, the TC programme has facilitated the training of more than 180 fellows in the fields of nuclear medicine, diagnostic imaging, radiostope and radiation treatment, radiation metrology and dosimetry, radiopharmacy, diagnostic radiology, molecular biology techniques and immunodiagnostics as well as tissue radiosterilization. The IAEA also organizes scientific visits and expert missions that focus on specific nuclear medicine topic areas, and provides on-site local training and expert advice. These training activities facilitate the transfer of skills and knowledge and help countries exchange information on new technologies and procedures.
In addition to the training supported by the TC programme, the IAEA works to ensure that ionizing radiation in nuclear medicine is used safely and effectively, in line with internationally recognized basic safety standards. The IAEA also produces educational and training material on the clinical applications and the appropriate use of the nuclear medicine both in the diagnostic and therapeutic fields. This material is available on the IAEA web site, in particular in the online "Human Health Campus", which was developed to serve professionals in radiation medicine and nutrition, including the nuclear medicine community.
Building Capacity in Health Care: How the IAEA Supports Training in Nuclear Medicine Professions
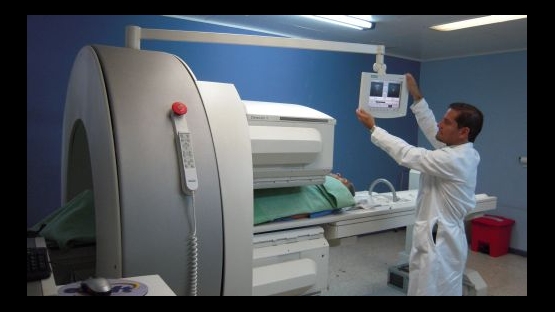
A multidisciplinary nuclear medicine team
Nuclear medicine professionals are individuals with extensive training in nuclear medicine across a range of disciplines. At the head of the multidisciplinary team is the nuclear medicine physician, a medical doctor who uses radioactive material as tracers in the human body to study the functions of various organs and to detect abnormalities. Nuclear medicine physicians make their diagnosis based on the diagnostic images obtained, providing useful information for the preparation of comprehensive treatment plans.
A certified nuclear medicine technologist assists the physician and is responsible for operating the equipment used to generate diagnostic images.
Medical physicists and radiopharmacists are an indispensable part of the team. The medical physicist is responsible of the areas of dosimetry, image quality, optimization, radiation safety, quality assurance and equipment management. While radiopharmacists prepare correct doses of radiopharmaceuticals and ensure their safety and efficacy.